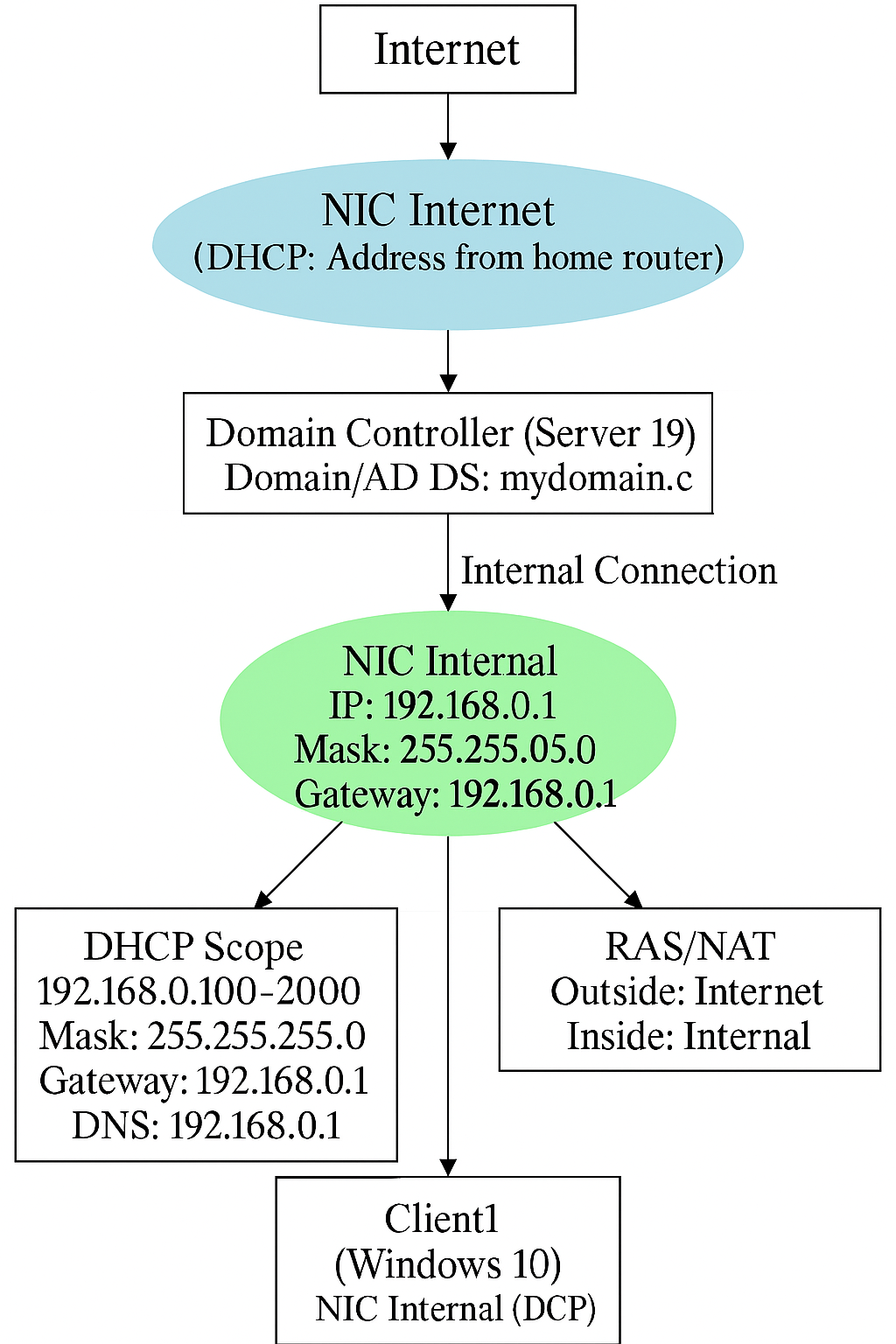
I created this flowchart to demonstrate how I set up the network for my Active Directory lab.
It shows a small practice network managed by a server called the Domain Controller (Windows Server 2019).
The server has two connections: one to the internet through a home router and another to a local network with a fixed IP address (172.16.0.1).
The Domain Controller assigns IP addresses to devices on the local network, provides internet access, and allows a Windows 10 computer to join the network group (called a domain) for easy management.
The first step involves creating a virtual machine (VM) using VMware Workstation and installing Windows Server 2019 as the operating system.
This VM will act as the central authority for the network, managing user access and enforcing security policies.
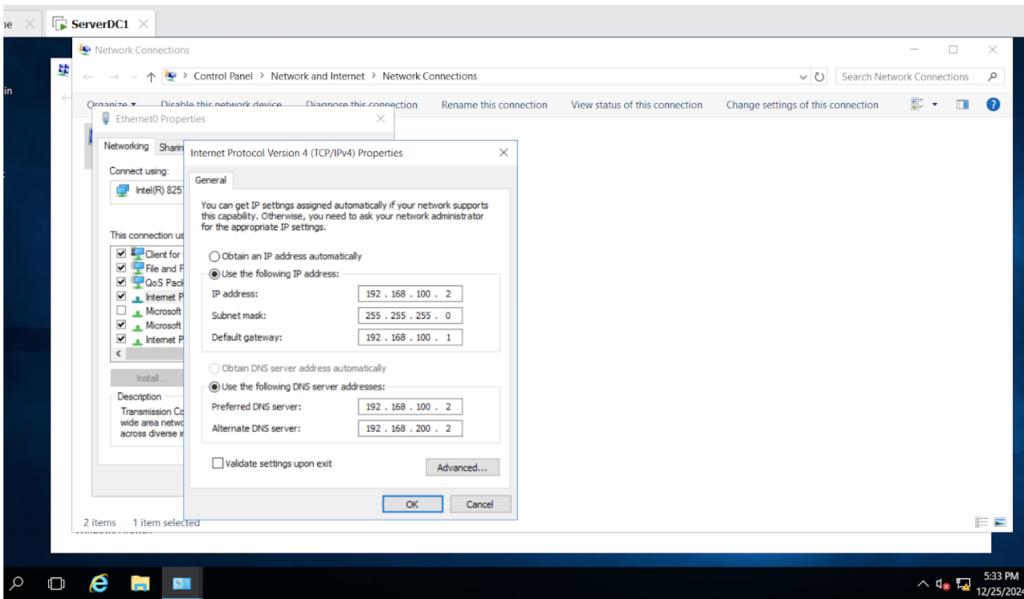
The next step is to set up the Network Interface Card (NIC) on the Domain Controller to manage connections for the private network and the internet.
This involves assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, and DNS settings.
Configuring the NIC properly ensures the Domain Controller can communicate smoothly with devices on the private network and access internet resources, which is important for Active Directory to work efficiently.
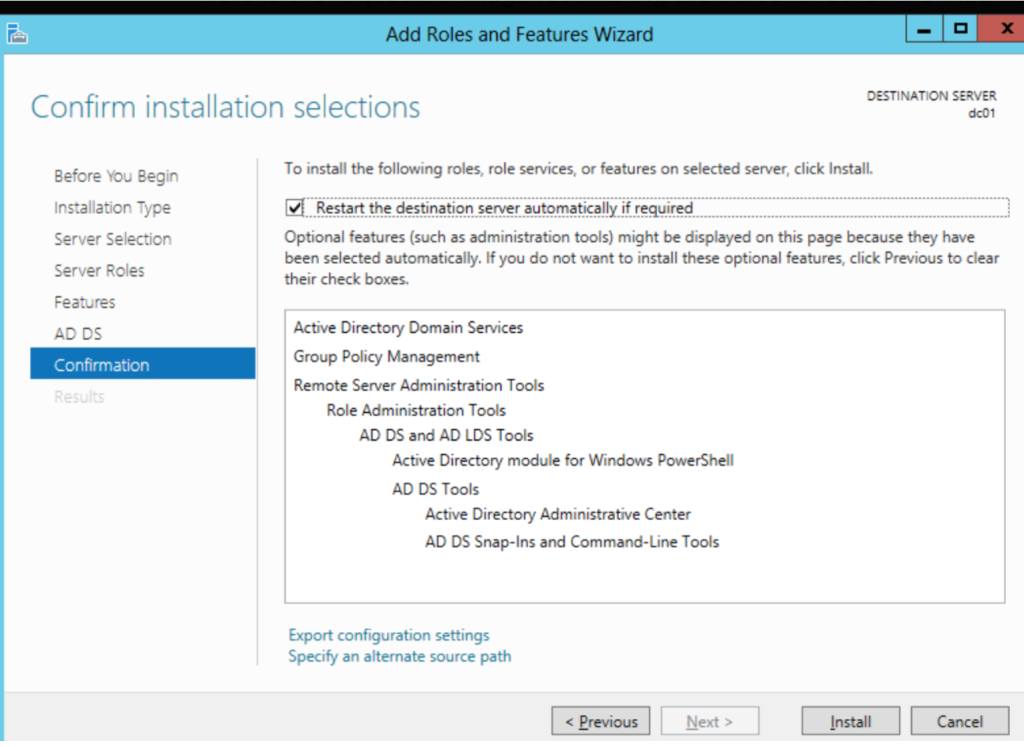
I am currently installing the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role on a Windows Server.
AD DS is a critical service that enables the server to function as a domain controller.
This allows for centralized user management, enforces security policies, and provides a structured framework for organizing network resources.
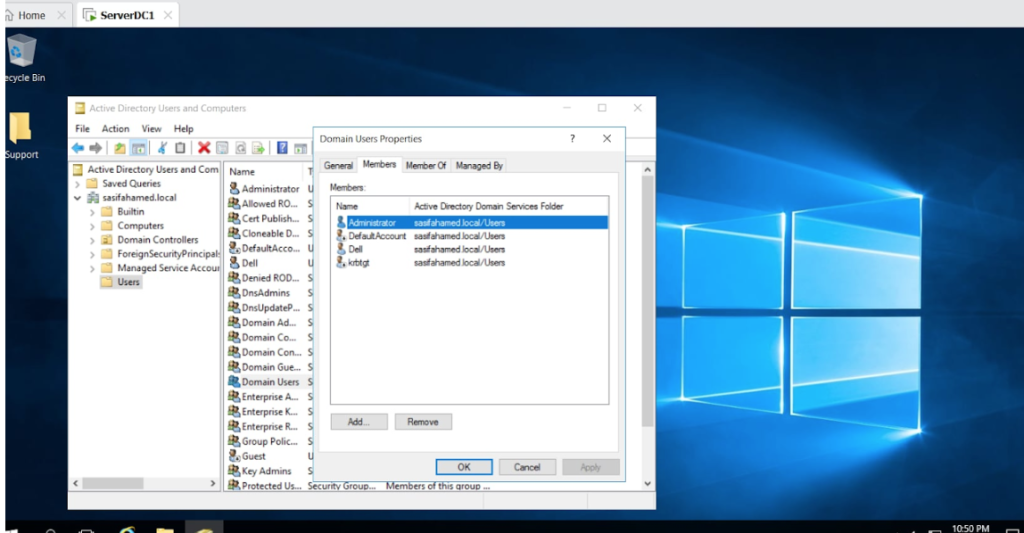
I am setting up a user account specifically for administrative access within the Active Directory domain.
This account, which is associated with my name, will oversee domain management.
Using a separate domain admin account is vital for maintaining security and proper oversight in the Active Directory environment.
It ensures that only authorized personnel perform critical administrative operations.
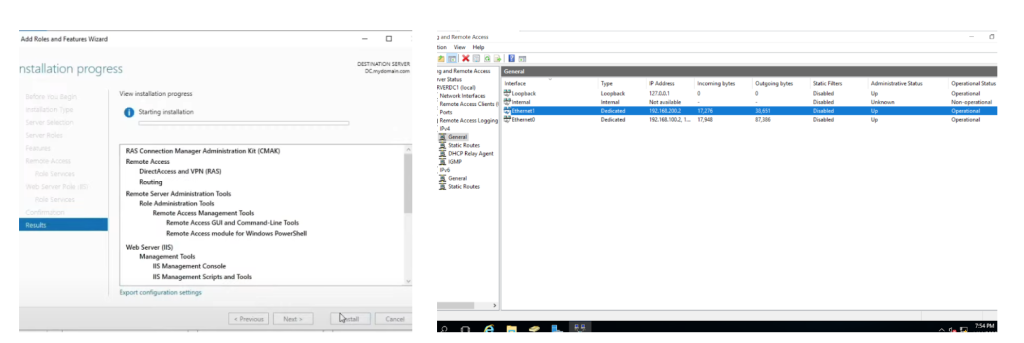
This step is about installing Routing and Remote Access Services (RAS) on the Domain Controller.
Setting up RAS NAT (Network Address Translation) allows the Domain Controller to act as a gateway, letting connected devices access the internet.
This helps provide internet access to devices on the private network.
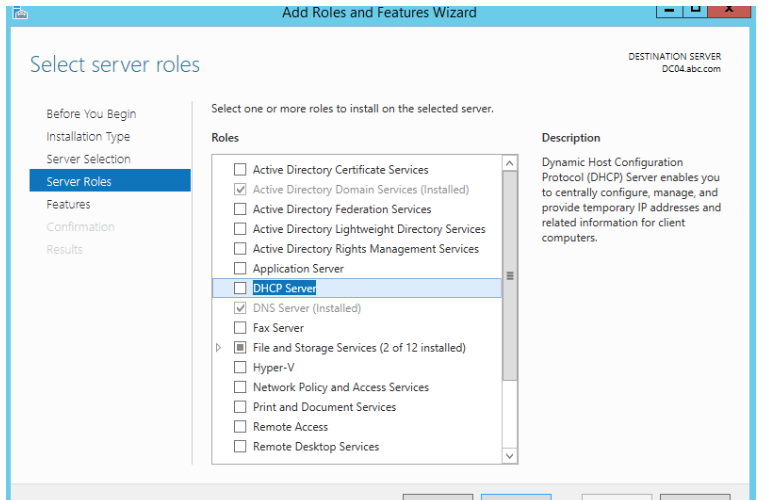
This step is about setting up the DHCP Server on the Domain Controller.
The DHCP Server automatically gives IP addresses to devices on the network, making it easier to manage.
With DHCP, devices get their IP settings automatically, so you don’t have to set them up manually.
This helps everything connect smoothly within the network.

This step is about setting up a DHCP Server Scope, which is a range of IP addresses that the server can give to devices on the network.
The scope helps automatically assign IP addresses so that devices can connect properly without needing manual setup.
It also includes other network settings like the subnet mask and lease time to manage connections efficiently.
